How to Take a Power Nap: Simple Tips That Actually Work
Introduction: What Is A Power Nap?
Ever hit that mid-afternoon slump where your eyelids feel like they weigh a ton and your brain refuses to cooperate? You’re not alone. That’s where a power nap comes in.
A power nap is a short sleep session, typically lasting 10 to 30 minutes, designed to boost your energy and alertness without leaving you groggy. Unlike longer naps that take you into deeper sleep stages, power naps keep you in the lighter sleep phases, allowing you to wake up refreshed and ready to tackle the rest of your day.
The concept isn’t just folk wisdom—a NASA study with long-haul flight crews found that pilots who took a nap, averaging 26 minutes, showed improved physiological alertness and performance compared to those who didn’t nap. When done correctly, power naps can sharpen your focus, improve your mood, enhance memory, and help you push through that afternoon energy dip. But timing and technique matter. This guide covers the basics of power napping and helps you power nap like a pro.
Want a Power Nap Schedule That Actually Works for You?
How Power Naps Affect Your Brain and Body
Power naps trigger specific changes in your brain and body that lead to measurable improvements in how you think, feel, and perform. Here’s what happens when you take a power nap and why it works.
What Happens During a Power Nap
If you keep your nap between 10 and 30 minutes, you stay in the “light sleep” zone without grogginess. This is technically known as Stage 1 and 2 of the non-REM cycle. According to the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, these stages allow your brain to rest without entering deep sleep, which is why you wake up feeling alert rather than groggy.
During this time:
- Napping helps scrub away adenosine, a chemical by-product of being awake that creates that heavy, tired feeling.
- While you rest, your brain is busy strengthening connections between neurons, which helps lock in memories.
- It allows your nervous system to switch gears from “fight or flight” to a restorative, healing mode.
- A quick snooze can actually lower your body’s stress response by dropping cortisol levels.
Brain Benefits
| Benefit | What Research Shows |
|---|---|
| Improved Memory | Power naps enhance both declarative memory (facts) and procedural memory (skills). According to Johns Hopkins Medicine , a 20-30 minute nap can boost memory function. |
| Enhanced Focus | Short naps restore attention and concentration, particularly helpful for tasks requiring sustained focus. |
| Better Decision-Making | Research from Sleep Medicine Reviews shows naps improve cognitive flexibility and problem-solving abilities. |
| Increased Creativity | Naps can enhance creative thinking by allowing your brain to make new connections between ideas. |
| Faster Reaction Time | Studies show reaction times improve significantly after a brief nap, which is important for tasks like driving. |
Physical Benefits
- Reduced fatigue: Even a 10-minute nap can significantly decrease feelings of tiredness
- Lower blood pressure: According to research presented at the American College of Cardiology, daytime napping helped reduce blood pressure
- Improved immune function: Brief naps support your immune system by reducing stress.
- Enhanced physical performance: Athletes often use power naps to boost reaction time and accuracy
- Better mood regulation: Naps help regulate emotions and reduce irritability
How to Take a Power Nap
Taking an effective power nap isn’t just about closing your eyes—it requires the right timing, duration, environment, and technique. Follow these simple steps to master the power nap.
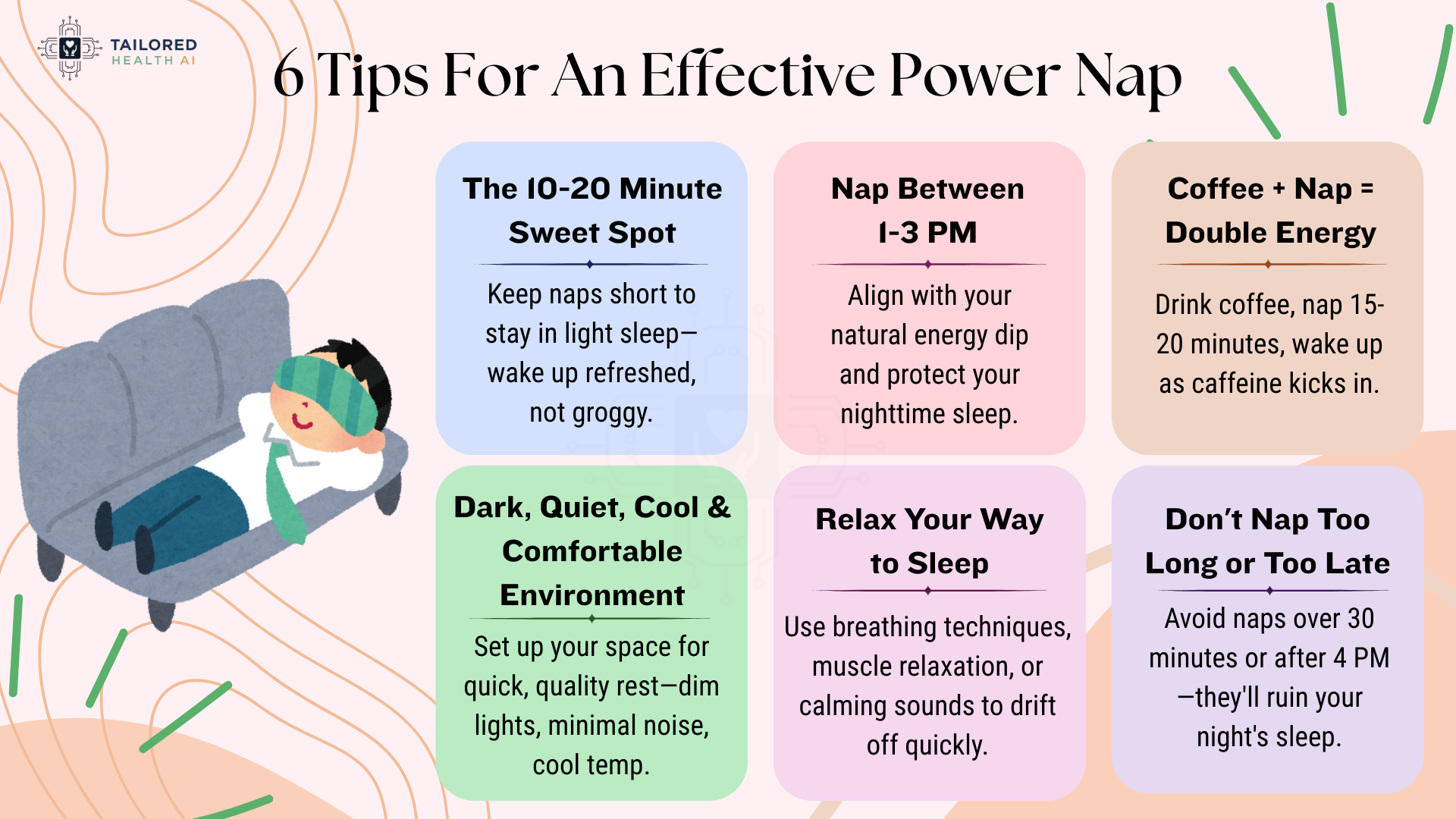
1. Ideal Length Of A Power Nap
The ideal power nap duration is 10-20 minutes. This keeps you in light sleep stages (Stage 1 and Stage 2), allowing you to wake up refreshed without grogginess.
2. Best Time to Power Nap
Ideal Window: 1:00 PM – 3:00 PM
Why this timing works:
- Aligns with your body’s natural circadian dip (usually 7-9 hours after waking)
- Coincides with the post-lunch energy slump
- Far enough from bedtime (6-7 hours before sleep)
- Won’t interfere with nighttime sleep
Timing Guidelines:
✅ Do:
- Nap in early afternoon (1-3 PM)
- Keep it at least 6-7 hours before bedtime
- Nap when you feel naturally tired
❌ Don’t:
- Nap after 4:00 PM
- Nap immediately after waking up
- Nap if you have insomnia (can worsen it)
3. Special Strategy: The Coffee Nap
Want to supercharge your power nap? Try the coffee nap technique.
How it works:
Research from the Sleep Foundation shows that drinking coffee immediately before a 15-20 minute nap can enhance alertness and cognitive performance better than either alone. Studies on sleepy drivers and shift workers found that caffeine combined with a nap improved alertness, logical reasoning, and performance tests.
Steps:
1. Quickly drink coffee or caffeinated tea.
2. Immediately lie down.
3. Set an alarm for 15-20 minutes.
4. Wake up with a double energy boost.
4. Creating the Perfect Nap Environment
Your environment makes or breaks your power nap success.
| Essential elements | Why It Matters | How to Achieve It |
|---|---|---|
| Darkness | Signals your brain to stay asleep. | Use an eye mask or blackout curtains. |
| Silence | Sudden sounds can ruin your rest. | Use a white noise machine or earplugs to mask distractions. |
| Cool temperature | Hot temperature doesn’t allow sleep. | Keep room at 60-67°F (15-19°C) per the National Sleep Foundation. |
| Comfort | Tension prevents relaxation. | Lie down or recline; loosen tight clothing. |
| No interruptions | Distractions prevent you from falling asleep. | Phone on silent, inform others you’re napping. |
5. Quick Tips to Fall Asleep Faster
Breathing techniques:
- 4-7-8 method: Inhale for 4 counts, hold for 7, exhale for 8
- Box breathing: Follow the “4-count” rule: inhale 4 counts, hold 4 counts, exhale 4 counts.
Breathing techniques:
- Progressive muscle relaxation: Systematically tighten and then release your muscles.
- Visualize a peaceful scene
- Listen to white noise or calming sounds
- Count backwards from 100
Important:
Don’t worry if you can’t fall asleep. Even resting quietly with eyes closed for 20 minutes provides benefits.
6. Common Power Nap Mistakes to Avoid
Master Your Power Naps and Nighttime Sleep
Bad Power Naps: Effects on Sleep
While power naps offer great benefits, doing them wrong can backfire. Here’s what happens when naps go bad and how to avoid these problems.
What Makes a Power Nap “Bad”?
- Napping too long (over 30 minutes)
- Napping after 4 PM.
- Napping when you’re not tired
- Using naps to replace nighttime sleep
Two Main Problems: Sleep Inertia and Nighttime Disruption
Problem 1: Sleep Inertia (The Grogginess)
When you nap longer than 30 minutes, you enter deep sleep. Waking from deep sleep causes sleep inertia—grogginess, confusion, and impaired performance lasting 15-60 minutes.
Signs you’re experiencing sleep inertia:
- Disorientation upon waking
- Difficulty concentrating
- Slower reaction times
- Increased irritability
According to the CDC’s National Institute for Occupational Safety and Health, this happens because your brain hasn’t fully transitioned out of deep sleep mode, and people can show slower reaction time, poorer short-term memory, and impaired reasoning.
Problem 2: Disrupted Nighttime Sleep
Late naps sabotage your nighttime rest.
| What You’re Doing Wrong | How It Affects Your Night’s Sleep |
|---|---|
| Napping after 4 PM | Difficulty falling asleep at bedtime |
| Napping over 30 minutes | Reduced sleep quality, and frequent night awakenings |
| Multiple daily naps | Fragmented nighttime sleep, and disrupted circadian rhythm |
| Napping when not tired | Delayed sleep onset, irregular sleep patterns |
Why Naps Can’t Replace Real Sleep
The National Sleep Foundation emphasizes that naps provide temporary alertness but can’t substitute for 7-9 hours of nighttime sleep. You miss complete sleep cycles, especially REM sleep, and confuse your body’s circadian rhythm.
Who Should Avoid Power Naps
| Who | Why Avoid |
|---|---|
| Insomnia Risk | Napping lowers your “sleep drive,” making it harder to fall asleep when you actually want to. |
| Those with sleep disorders | Can worsen sleep apnea or circadian rhythm problems. |
| Evening shift workers | May have trouble staying awake during work hours. |
The Bottom Line on Bad Naps
Power naps are tools, not crutches. When used correctly—short duration (10-20 minutes), right timing (early afternoon), and appropriate frequency (occasional, not daily)—they enhance your day. Incorrect napping habits do more harm than good. The key is understanding your body’s sleep needs and respecting your natural circadian rhythm rather than fighting against it.

